Curriculum Overview
The Medical Undergraduate Program (MDUP) curriculum is designed to train medical students towards developing exit competencies within the CanMEDS framework.
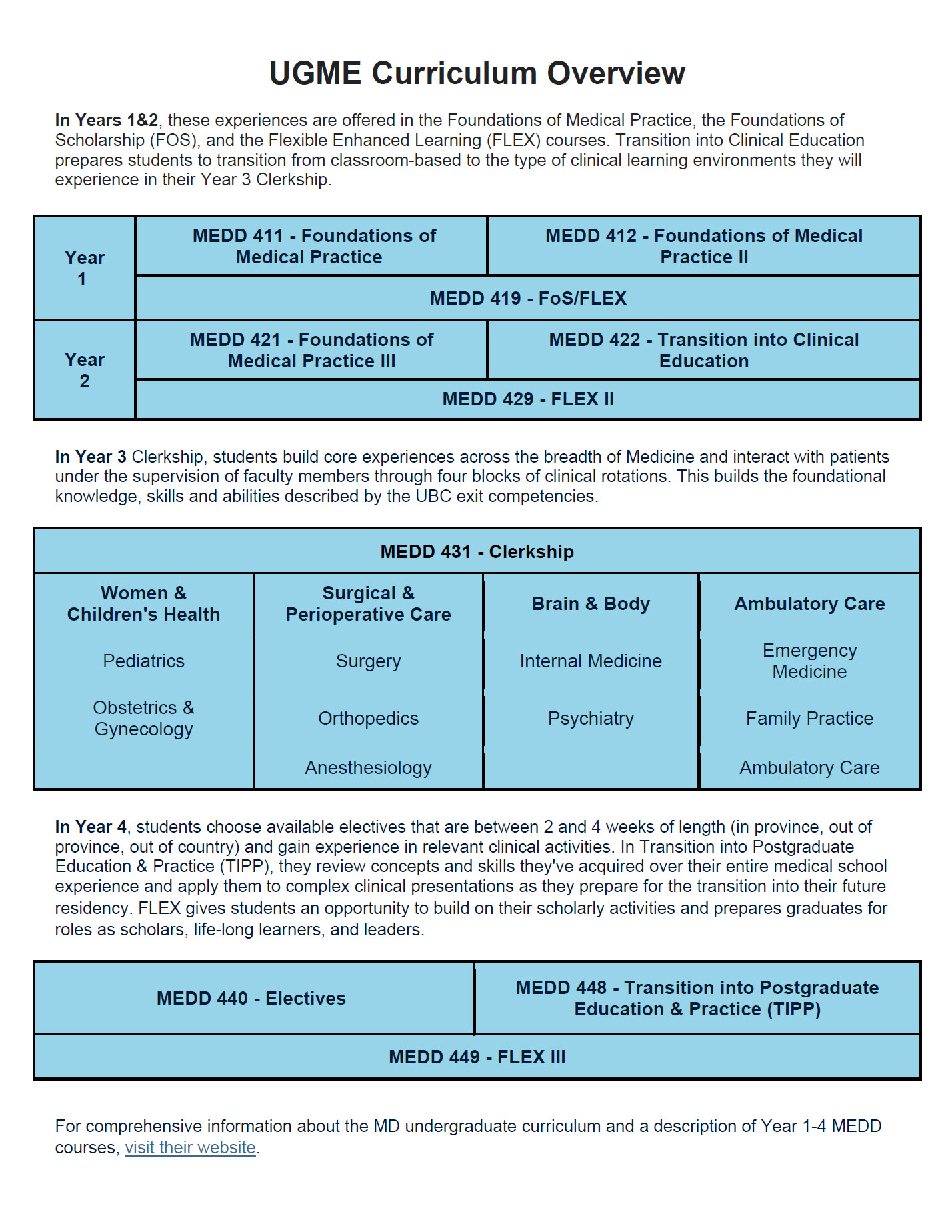
MDUP Curriculum Overview
In the first two years of the Medical Undergraduate Program (MDUP), students explore clinical presentations of increasing complexity through case-based learning and the clinical skills curriculum. They also pursue a variety of learning experiences designed to enhance scholarship, engagement, and social accountability.
This is followed in the third year by building experiences across the breadth of Medicine and interacting with patients through four blocks of clinical rotations and in the fourth year by rotating through electively chosen clinical rotations.
Click on the image to download a quick overview of the courses that make up the MDUP program Years 1-4.
For a more comprehensive explanation of courses and curriculum, please explore the MDUP Curriculum page.
The Years 3 & 4 Resources for Clinical Faculty and Residents curated page provides a comprehensive list of curriculum and assessment resources for Year 3 and Year 4 Clinical Preceptors including Workplace Based Assessment (WBA) Orientation, Clinical Procedures and Patient Encounters, and samples of End of Rotation (EOR), Clinical Performance Review (CPR) and End of Elective (EOE) forms.
PGME Curriculum Overview
Like all Royal College Postgraduate Medical Education (PGME) programs, UBC is transitioning to Competency Based Medical Education (CBME). Competence by Design (CBD) is the Royal College’s multi-year, medical education initiative involving the implementation of a CBME approach to education and assessment in residency training and specialty practice in Canada.
CBME is an approach to physician development that focuses on the process and outcomes of training, and makes the achievement of competencies more visible and measurable. It is a model designed to be adapted and restructured for each individual resident. In CBME, coaching and feedback occurs in the moment and in relation to specific tasks, whereas in a traditional model of postgraduate medical education, assessments occur after a set period of time and often removed from daily clinical work.


The College of Family Physicians of Canada (CFPC) establishes the standards for and accredits postgraduate family medicine training in Canada’s 17 medical schools. It reviews and certifies continuing professional development programs and materials that enable family physicians to meet certification and licensing requirements.
The CFPC has adopted the Triple C Curriculum for their postgraduate residency training program. The Triple C Curriculum is also competency-based that is based on the three principles of:
-
- Comprehensive Care
- Continuity of education and patient care, and
- Centred in Family Medicine
Throughout their training, residents develop their competencies in different areas through ongoing structured assessment and self-reflection.