Assessment of Learners
The programmatic assessment system provides valid, reliable and timely assessments of the competence of trainees to guide progress and promotion decisions and to motivate, direct and support learners.
MDUP Assessment Overview
Assessment in the MD Undergraduate Program (MDUP) is built on principles of programmatic assessment where a mix of assessment methods or modalities are used in each course. The programmatic assessment model maintains consistency in the assessment modalities used (Progress Tests, Written Exams, Objective Structured Clinical Exams, Workplace Based Assessment, and Portfolio) across the 4-year program.
This model is integrative, developmental, and provides regular, appropriate, and, timely feedback to students and faculty.
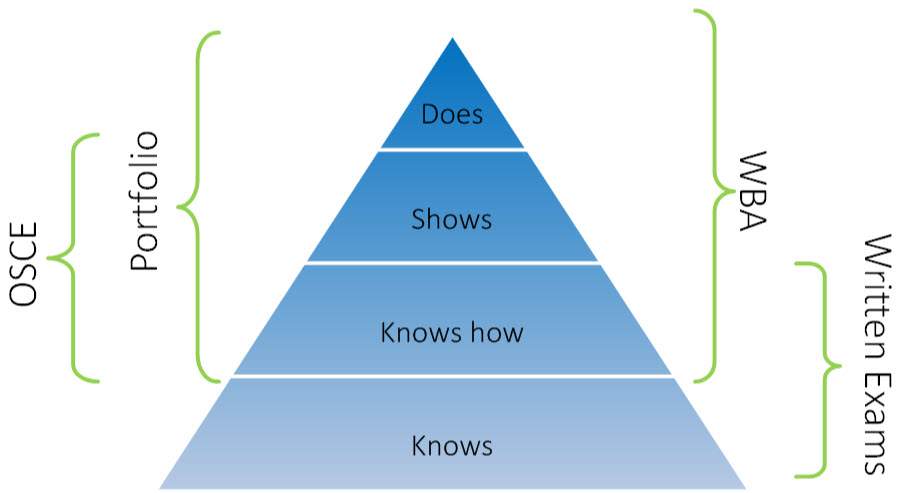
Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE)
OSCEs assess clinical skills using standardized simulated clinical scenarios. Students perform specific clinical tasks such as history-taking, physical examination or counselling, reflective of an appropriate level of skill development. A pre-set number of OSCE stations in years 2 & 4 are required to be passed to pass the OSCE. Year 1 & 3 OSCEs include verbal feedback from the examiner and are offered for practice and learning; students are required to complete these.
Portfolio
Students are placed in groups of 7-9 students, each with a designated faculty portfolio coach. These portfolio groups meet several times per year year to explore and reflect on what students are learning and seeing in practice. In addition, students also submit written assignments that coaches provide feedback on.
Written Exams
Course Written Exams are based on multiple choice questions. Their purpose is to assess applied knowledge related to the learning objectives in a course. Students must achieve a minimum cumulative score of 60% across all course written exams to pass the course.
Progress Tests are based multiple choice questions which are set at exit (graduate) competency level. The same exam is taken multiple times a year across all four years, allowing students to track their progress in the use of applied knowledge over time.
Workplace Based Assessment (WBA)
Multiple observations of student’s knowledge, skills and behaviour in the workplace are conducted iteratively in each course.
WBA focuses on assessment of students' demonstrated knowledge, skills and attitudes; provides on-going, effective feedback to students; maps students' developmental progression towards achieving Year 3 milestones; allows assessors to identify students with academic or professionalism concerns; identifies students in need of extra assistance so the appropriate supports can be provided. Narrative feedback and suggestions for improvement are built into WBA.
Students must achieve the Course Learning Outcomes assessed by WBA to pass a course.
The Years 3 & 4 Workplace Based Assessment (WBA) Orientation module linked in the Resources section below provides a comprehensive guide to WBA including filling out a Direct Observation (DO) form.
The Years 3 & 4 Resources for Clinical Faculty and Residents curated page provides a comprehensive list of curriculum and assessment resources for Year 3 and Year 4 Clinical Preceptors including Workplace Based Assessment (WBA) Orientation, Clinical Procedures and Patient Encounters, and samples of End of Rotation (EOR), Clinical Performance Review (CPR) and End of Elective (EOE) forms.
PGME Assessment Overview
Assessment in Postgraduate Medical Education (PGME) is program specific. Assessment methods can involve a mix of formative and summative tools.
Competency-based medical education (CBME) is an outcomes-based approach to the design, implementation, assessment and evaluation of a medical education program using an organizing framework of competencies (e.g., CanMEDS 2015).
CBME is a framework of education which focuses on both the process & outcomes of training. The outcomes serve as signposts and frequent, low-stakes assessments from clinical educators track residents’ progression towards competence. In other words, residents’ progression through rotations is dependent on their achieving pre-determined competencies rather than reaching the end of a rotation.
Competence by Design (CBD) is the Royal College’s multi-year, medical education initiative involving the implementation of the CBME approach to education and assessment in residency training and specialty practice in Canada.
On the diagram below, click on the ‘i’ icons for more information about each part of the CBD process.
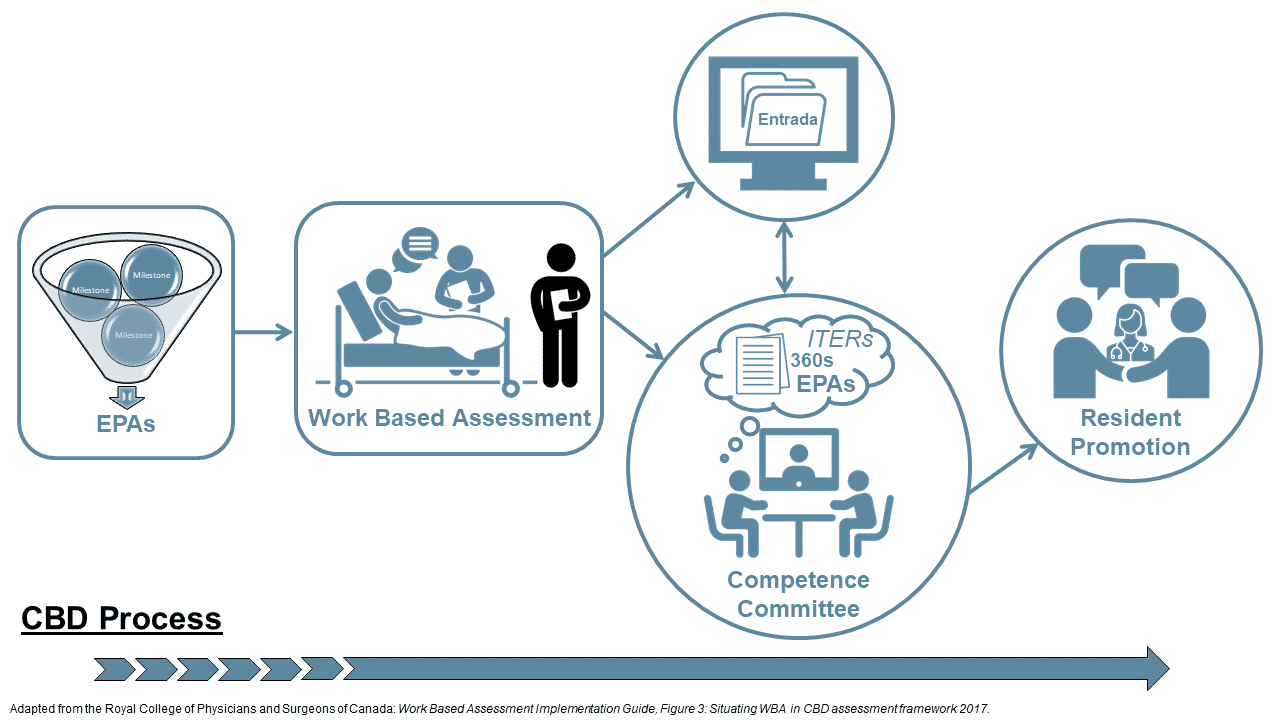
EPAs and Milestones
EPAs are the key tasks or activities that a resident needs to be able to perform (e.g. run a clinic). Each EPA contains Milestones.
Milestones are specific, measurable and observable components of an EPA (e.g. intubate an airway under supervision), required to fully demonstrate EPA achievement
Work Based Assessment (WBA)
The goal of WBAs is for frontline clinical teachers to observe and document authentic observations of a resident’s performance in the workplace on a regular basis.
In CBD, WBAs are EPA assessments, and are designed to provide specific, timely feedback to learners on their skill progression and inform EPA achievement decisions of the competence committee
Entrada
Entrada is the system used to collect and track a resident’s EPAs at UBC.
Competence Committee
Competence Committees review each residents’ EPAs and other assessment data, then recommend promotion and/or further support for the resident.
Resident Promotion
Resident promotion is when the competence committee recommends that the resident progress to the next stage.
Royal College Exams for specialties and College of Family Physicians of Canada (CFPC) exams occur near the end of training. Possible Assessment Methods used in postgraduate training programs include:
– In Training Evaluation Reports (ITERs) – Royal College
– In Training Assessment Reports (ITARs) – Family Medicine
– Entrustable Professional Activities (EPAs) – Royal College
– Field Notes – Family Medicine
For a more comprehensive look at assessment in Family Medicine, explore the page Resident Assessment for Learning.